The History of OxyContin: From Inception to Controversy
The History of OxyContin: From Inception to Controversy
OxyContin, a powerful prescription painkiller, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential for abuse and addiction. In order to understand the controversy surrounding this drug, it is important to examine its history, types, and uses.
The story of OxyContin begins in the late 1980s when the pharmaceutical company Purdue Pharma developed a new formulation of the opioid drug oxycodone. The goal was to create a time-release medication that would provide long-lasting pain relief for patients suffering from chronic conditions. This new formulation was named OxyContin, and it was marketed as a breakthrough in pain management.
When OxyContin was first introduced to the market in 1996, it was seen as a game-changer in the field of pain medicine. Doctors were hopeful that this medication could provide relief to patients who had previously been unable to find effective treatment for their chronic pain. The time-release mechanism of OxyContin allowed for a steady release of the drug over a 12-hour period, providing consistent pain relief for patients.
However, as OxyContin gained popularity, reports of abuse and addiction began to emerge. The drug’s high potency and extended-release formulation made it attractive to individuals seeking a powerful high. Some people discovered that by crushing the tablets, they could bypass the time-release mechanism and experience an intense and immediate euphoria.
This abuse potential led to a wave of addiction and overdose cases across the United States. OxyContin became known as “hillbilly heroin” due to its prevalence in rural areas, where addiction rates skyrocketed. The drug’s popularity also led to an increase in illegal activities, such as doctor shopping and the diversion of prescription medications for illicit use.
In response to the growing concerns surrounding OxyContin, Purdue Pharma faced mounting pressure to address the issue. In 2010, the company reformulated the drug to make it more difficult to crush or dissolve, aiming to deter abuse. The new formulation made the tablets harder to manipulate, but it did not entirely eliminate the risk of misuse.
Despite these efforts, the controversy surrounding OxyContin continues to this day. Many individuals who became addicted to the drug have turned to illicit substances, such as heroin, when their access to OxyContin was restricted. The opioid crisis, fueled in part by the widespread misuse of drugs like OxyContin, has become a public health emergency in the United States.
As the debate over OxyContin rages on, policymakers, healthcare professionals, and communities are grappling with how to address the issue. Efforts to increase access to addiction treatment, improve prescribing practices, and educate the public about the risks of opioid medications are being implemented, but progress is slow.
Ultimately, the history of OxyContin serves as a cautionary tale about the dangers of powerful prescription drugs and the need for comprehensive strategies to combat addiction. As the medical community continues to search for safer alternatives for pain management, it is crucial to learn from the mistakes of the past and prioritize the well-being of patients above all else.
OxyContin is a powerful opioid medication that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential for misuse and addiction. While it can be an effective tool for managing pain, it is crucial to understand the risks and potential consequences associated with its use.
When taken as prescribed, OxyContin works by binding to specific receptors in the brain and spinal cord, blocking pain signals and providing relief. However, its potency and extended-release formulation make it particularly attractive to those seeking to misuse or abuse opioids.
One of the main concerns with OxyContin is its high potential for addiction. The drug activates the brain’s reward system, leading to feelings of euphoria and relaxation. Over time, individuals may develop a tolerance to the drug, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effect. This can quickly spiral into dependence and addiction.
In addition to its addictive properties, OxyContin carries several other risks. One significant danger is the potential for overdose. The extended-release formulation of OxyContin means that a large amount of the drug is released into the body over an extended period. If someone were to crush or chew the tablets, it could release the entire dose at once, leading to a potentially fatal overdose.
Furthermore, the misuse of OxyContin can have severe consequences for individuals’ physical and mental health. Prolonged use of opioids can lead to respiratory depression, constipation, nausea, and drowsiness. It can also increase the risk of developing mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Due to the growing concern surrounding OxyContin abuse and addiction, there have been efforts to regulate its use more strictly. Physicians are now required to closely monitor patients who are prescribed OxyContin and regularly assess the need for continued use. Additionally, various educational programs and initiatives have been implemented to raise awareness about the risks associated with OxyContin and promote safer alternatives for pain management.
It is important for individuals prescribed OxyContin to follow their healthcare provider’s instructions carefully and be aware of the potential risks and side effects. Open communication with healthcare professionals is crucial to ensure the safe and effective use of this medication.
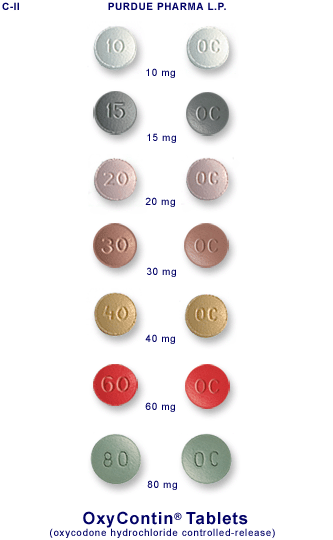
The Types of OxyContin
OxyContin is available in various strengths, ranging from 10mg to 80mg. The dosage prescribed depends on the severity of the pain and the patient’s tolerance to opioids. It is important to note that OxyContin should only be used under the supervision of a healthcare professional and according to the prescribed dosage.
When it comes to pain management, OxyContin is one of the most commonly prescribed medications. It belongs to a class of drugs known as opioids, which are powerful pain relievers. OxyContin contains the active ingredient oxycodone, which works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, reducing the transmission of pain signals.
The different strengths of OxyContin allow healthcare professionals to tailor the dosage to each individual patient’s needs. For mild to moderate pain, a lower strength, such as 10mg or 20mg, may be prescribed. These lower doses are often used when starting OxyContin treatment or when the patient has a lower tolerance to opioids.
For more severe pain, higher strengths of OxyContin may be necessary. Dosages of 40mg or 80mg are typically reserved for patients who have developed a tolerance to opioids or who require stronger pain relief. These higher doses should only be used under close medical supervision, as they carry a higher risk of side effects and potential for misuse.
It is important for patients to follow their healthcare professional’s instructions when taking OxyContin. Taking a higher dosage than prescribed or using the medication without a prescription can lead to serious health consequences, including overdose and addiction. OxyContin should never be crushed, chewed, or dissolved, as this can release the entire dose at once and increase the risk of overdose.
In addition to the different strengths, OxyContin may also be available in different formulations. The extended-release formulation is designed to provide long-lasting pain relief, with effects that can last up to 12 hours. This allows patients to take fewer doses throughout the day, improving convenience and reducing the risk of medication errors.
Overall, the availability of various strengths and formulations of OxyContin allows healthcare professionals to customize treatment plans for their patients, ensuring that they receive the most effective and appropriate pain relief. However, it is crucial for patients to use OxyContin responsibly and under medical supervision to minimize the risks associated with opioid use.
In addition to its primary use for pain management, OxyContin has been found to be beneficial in other medical conditions as well. One such condition is palliative care, where OxyContin can be used to alleviate the suffering of terminally ill patients. By providing relief from severe pain, OxyContin allows these patients to live their remaining days in comfort and dignity.
Furthermore, OxyContin has been found to be effective in managing pain associated with certain neurological disorders. Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, neuropathy, and fibromyalgia can cause debilitating pain that significantly impacts a person’s daily life. OxyContin, when used appropriately, can help alleviate these symptoms and improve the overall functioning of individuals with these conditions.
Moreover, OxyContin has shown promise in the field of psychiatry. It has been used as an adjunct treatment for individuals with treatment-resistant depression. In some cases, depression can be so severe that traditional antidepressant medications are not effective. OxyContin, when used in combination with other treatments, has been found to provide relief from depressive symptoms and improve the quality of life for these patients.
Additionally, OxyContin has been used in certain surgical procedures to provide effective pain control. For instance, in major orthopedic surgeries or reconstructive surgeries, where the post-operative pain can be intense, OxyContin can be administered to ensure adequate pain relief. This not only helps patients recover more comfortably but also promotes faster healing and rehabilitation.
It is important to note that the uses of OxyContin extend beyond these examples, and its potential benefits are continually being explored in various medical fields. However, it is crucial to emphasize that the use of OxyContin should always be guided by a healthcare professional, taking into consideration the potential risks and benefits for each individual patient.
Despite the initial optimism surrounding OxyContin, it quickly became apparent that the drug had a dark side. Doctors began prescribing it at an alarming rate, often for conditions that did not warrant such a potent medication. Patients were given high doses of OxyContin for minor injuries or short-term pain, leading to a widespread misuse of the drug.
One of the main reasons for the rapid rise in OxyContin prescriptions was the aggressive marketing tactics employed by Purdue Pharma. The company heavily promoted the drug to doctors, offering incentives and downplaying the risks of addiction. As a result, many physicians were convinced that OxyContin was a safe and effective solution for their patients’ pain management needs.
However, as the number of prescriptions soared, so did the number of people struggling with addiction. OxyContin’s extended-release formula, which was intended to provide long-lasting relief, also made the drug highly attractive to those seeking a quick and intense high. Users quickly discovered that crushing or dissolving the pills would bypass the time-release mechanism, resulting in a powerful and immediate euphoria.
The widespread abuse of OxyContin soon caught the attention of law enforcement and public health officials. Reports of overdoses and deaths associated with the drug began to emerge, painting a grim picture of the consequences of OxyContin misuse. It became clear that the drug was not the safe alternative it was initially touted to be.
In response to the growing crisis, regulatory agencies and lawmakers took action to curb the misuse of OxyContin. Purdue Pharma faced numerous lawsuits and investigations for their deceptive marketing practices, eventually leading to a settlement of over $600 million in 2007. The company was also required to reformulate OxyContin to make it more difficult to abuse.
Despite these efforts, the damage had already been done. OxyContin had unleashed a wave of addiction and devastation across the country, leaving countless individuals and communities in its wake. It served as a stark reminder of the dangers of overprescribing and the need for greater oversight in the pharmaceutical industry.The controversy surrounding OxyContin continued to escalate as more evidence of its detrimental effects came to light. Studies revealed that the drug’s high potency and addictive properties made it a prime target for abuse and misuse. Individuals who initially sought pain relief found themselves trapped in a cycle of dependence, leading to devastating consequences for both their physical and mental well-being. Moreover, the aggressive marketing tactics employed by Purdue Pharma only exacerbated the problem. The company strategically targeted healthcare professionals, offering incentives and downplaying the risks associated with OxyContin. As a result, doctors were more likely to prescribe the drug, often in higher doses and for longer durations than necessary. This overprescribing contributed to the widespread availability of OxyContin on the black market and fueled the opioid epidemic that ravaged communities across the country. The impact of OxyContin abuse extended far beyond individual lives. Families were torn apart as loved ones succumbed to addiction or suffered fatal overdoses. Communities struggled to cope with the financial burden of treating addiction and providing support services for affected individuals. The crisis also strained healthcare systems, as hospitals and clinics became inundated with patients seeking treatment for opioid addiction. In response to the mounting concerns, regulatory bodies and law enforcement agencies began to take decisive action. Lawsuits were filed against Purdue Pharma and other pharmaceutical companies involved in the opioid crisis, accusing them of deceptive marketing practices and failure to adequately warn about the risks of their products. These legal battles exposed the extent of Purdue Pharma’s misconduct and led to substantial financial penalties. The company’s reputation was irreparably damaged, and public trust in the pharmaceutical industry was significantly undermined. As the controversy surrounding OxyContin unfolded, it became clear that the issue extended far beyond the actions of a single company. The opioid crisis highlighted the systemic flaws in the healthcare system, including the overreliance on prescription painkillers, inadequate regulation, and insufficient support for addiction treatment. Addressing these issues required a comprehensive approach, involving not only legal action against pharmaceutical companies but also increased access to alternative pain management strategies, improved education for healthcare professionals, and enhanced support for individuals struggling with addiction. In conclusion, the controversy surrounding OxyContin was a stark reminder of the devastating consequences that can arise from the unchecked pursuit of profit in the pharmaceutical industry. The drug’s high potential for abuse, coupled with aggressive marketing tactics, led to widespread addiction and contributed to the opioid crisis that continues to plague the United States. The fallout from this controversy serves as a powerful call to action, urging society to reevaluate its approach to pain management, addiction treatment, and the regulation of pharmaceutical products.




