let’s talk about ativan Lorazepam vs alprazolam, How Lorazepam and Alprazolam Works, where to buy Lorazepam, connection btween ativan and lorazepam, How Many Lorazepam Equals a Xanax?

Introduction to Lorazepam and Alprazolam
Lorazepam and alprazolam are both well-known medications classified under the benzodiazepine family, which are predominantly utilized to treat anxiety and panic disorders. Lorazepam, marketed under the brand name Ativan, and alprazolam, known as Xanax, have garnered significant attention due to their effectiveness and widespread usage in psychiatric treatments. These medications work by enhancing the inhibitory effects of neurotransmitters within the brain, thereby producing a calming effect that alleviates symptoms associated with anxiety disorders.
The development of lorazepam dates back to the early 1970s, when it was introduced to manage anxiety, insomnia, and preoperative sedation. With its relatively rapid onset of action, lorazepam quickly gained popularity for providing effective short-term relief from anxiety. Similarly, alprazolam was developed shortly after and received approval in the late 1970s. It is particularly noted for its efficiency in treating panic disorders and generalized anxiety disorder. The role these medications play in mental health treatment cannot be underestimated, as they have helped millions of people cope with debilitating symptoms of anxiety.
Understanding both lorazepam and alprazolam is essential, not only for healthcare providers but also for patients seeking relief from anxiety-related issues. Knowledge about the potential benefits, dosage, side effects, and best practices for use is crucial for ensuring effective treatment. With the ongoing dialogue about mental health, the significance of benzodiazepines like lorazepam and alprazolam is increasingly highlighted, underscoring the need for well-informed decisions regarding their use. An informed perspective aids in making the right choices to promote mental well-being while considering possible risks associated with these medications.
How Lorazepam Works
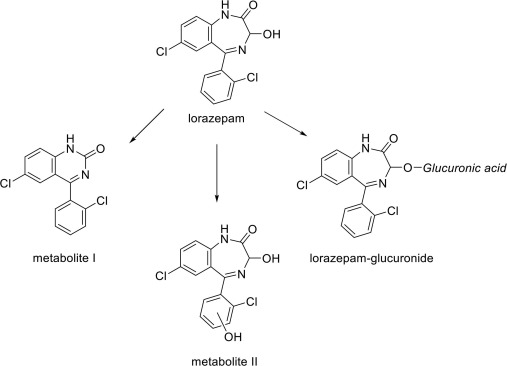
Lorazepam is a medication classified as a benzodiazepine, which primarily operates by modulating the activity of a neurotransmitter known as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA functions as the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS), playing a critical role in reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system. When Lorazepam is administered, it binds to specific sites on the GABA-A receptor, enhancing the pharmacological effects of GABA. This interaction increases the frequency of chloride channel openings, resulting in hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic neurons. Consequently, this mechanism produces significant anxiolytic, sedative, and anticonvulsant effects.
One of the primary indications for Lorazepam usage is for the relief of anxiety. By amplifying the effects of GABA, Lorazepam effectively diminishes feelings of tension and apprehension, promoting a sense of calm and relaxation. This makes it a frequent choice for treating generalized anxiety disorder or agitation caused by stress and trauma. Beyond anxiety, Lorazepam is also utilized for its sedative properties, often prescribed to help with sleep disturbances or as a pre-anesthetic agent before surgical procedures. In particular, its rapid onset of action and relatively short half-life make it suitable for outpatient settings.
In addition to anxiety and sedation, Lorazepam is indicated for the management of seizures, particularly status epilepticus, where rapid intervention is necessary to prevent complications. The effectiveness of Lorazepam in these scenarios is largely attributed to its ability to restore balance within the GABAergic system, thereby dampening excessive neuronal firing. As such, Lorazepam remains an integral medication within the therapeutic armamentarium for anxiety relief, sedation, and seizure control.
How Alprazolam Works
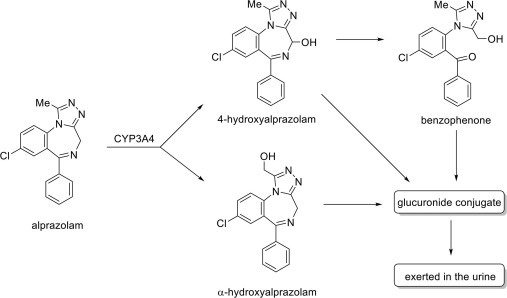
Alprazolam, a medication belonging to the benzodiazepine class, primarily acts on the central nervous system, exerting its therapeutic effects through potentiation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter known for its inhibitory properties. Both Alprazolam and Lorazepam work by enhancing GABAergic activity, which leads to anxiolytic, sedative, and muscle relaxant effects. Despite their similarities, Alprazolam is distinct in its clinical application and pharmacokinetics, making it uniquely beneficial for certain conditions.
The mechanism of action for Alprazolam involves binding to the benzodiazepine site on the GABA-A receptor, thereby increasing the frequency of channel opening events in response to GABA. This modulation enhances inhibition within neural circuits, resulting in reduced anxiety and a calming effect on the brain. Notably, Alprazolam is recognized for its rapid onset of action, often providing relief from anxiety and panic attacks within minutes to hours of administration. This swift response is particularly valuable in emergency and acute care settings.
Alprazolam is primarily indicated for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and panic disorder. Its efficacy for panic disorder is well-documented, as the rapid action helps manage overwhelming feelings of dread, making daily functioning more manageable for individuals suffering from this condition. However, potential side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, and cognitive impairments should be monitored closely. Additionally, long-term use can lead to tolerance and dependence, necessitating careful management by healthcare providers.
In conclusion, while both Alprazolam and Lorazepam serve important roles in anxiety management through their effects on GABA transmission, Alprazolam’s quick onset and specific indications for panic disorders highlight its unique profile among benzodiazepines.
Dosage and Administration: How to Take Lorazepam
Lorazepam is a medication commonly prescribed to manage anxiety disorders, insomnia, and other conditions related to anxiety. The recommended dosage of Lorazepam varies based on the individual’s age, the condition being treated, and other personal health factors. Typically, the standard initial dose for adults ranges from 1 to 3 mg, divided into two or three doses throughout the day. A healthcare provider will often tailor the dosage to ensure optimal efficacy while minimizing the potential for side effects.
When taking Lorazepam, it is crucial to adhere to the prescribed guidelines. The medication can be taken with or without food; however, utilizing a consistent method of ingestion can aid in maintaining stable blood levels of the drug. Some individuals may experience an increased incidence of gastrointestinal side effects when taken on an empty stomach, so taking it with food might help alleviate these symptoms.
For the elderly or those with liver conditions, special considerations regarding dosage and administration are necessary. The onset of hepatic impairment can diminish the elimination of Lorazepam, leading to a higher risk of accumulation and toxicity. Thus, healthcare providers generally recommend starting with a lower dosage and adjusting carefully based on the patient’s response. For this vulnerable population, dosage adjustments may reduce the likelihood of adverse effects while still providing therapeutic benefits.
It is important never to exceed the prescribed dose or duration of treatment, as prolonged use can lead to physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms upon cessation. Patients should also avoid mixing Lorazepam with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants without consulting a healthcare provider, as this can exacerbate sedative effects and lead to dangerous outcomes.
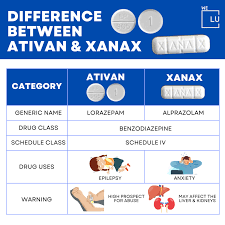
Comparative Analysis: Lorazepam vs Alprazolam
Lorazepam and alprazolam are both medications belonging to the benzodiazepine class, commonly used for managing anxiety disorders. However, they exhibit differences in efficacy, onset of action, half-life, side effects, and potential for dependency, making it important to understand these distinctions when considering treatment options.
In terms of efficacy, lorazepam is often prescribed for its effectiveness in treating acute anxiety symptoms and is sometimes recommended for patients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Alprazolam, on the other hand, is frequently utilized for panic disorder due to its potent anxiolytic properties. The choice between these medications can significantly depend on the patient’s specific anxiety-related symptoms and personal medical history.
The onset of action varies between the two medications. Alprazolam typically has a more rapid onset—taking effect within 30 minutes to an hour—making it suitable for situations requiring prompt relief from acute anxiety symptoms. Lorazepam, while still effective, may take slightly longer to begin working. Understanding these differences can aid patients in managing expectations related to their treatment.
When considering half-life, lorazepam has an average half-life of 10 to 20 hours, whereas alprazolam’s half-life ranges from 6 to 12 hours. This distinction plays a crucial role in determining the frequency of dosing and the potential for accumulation in the body, which can influence both therapeutic effects and the risk of adverse effects.
Side effects for both medications include drowsiness, dizziness, and potential cognitive impairment. However, alprazolam may carry a higher risk for withdrawal symptoms and dependency due to its shorter half-life and potency. Understanding these risks is essential when discussing treatment with healthcare providers and ensuring that patients receive the most suitable medication for their condition.
Is Lorazepam Ativan? Exploring Name Confusion
Lorazepam is a medication that is widely recognized for its efficacy in treating anxiety and insomnia. However, there is often confusion surrounding its identity, particularly regarding its brand name, Ativan. It is essential to clarify that Lorazepam is the generic name of the drug, while Ativan is the brand name under which it is marketed. This differentiation between generic and brand names is critical for both healthcare providers and patients, as it helps to avoid misunderstandings when prescriptions are being filled.
The confusion regarding drug names can lead to various issues, including the potential for medication errors. For instance, patients unfamiliar with the terminology might not realize that Lorazepam and Ativan refer to the same substance. Such misunderstandings can complicate treatment regimens and may result in the misuse or overuse of the medication. Hence, it is imperative that individuals understand the names associated with their prescriptions to ensure safe and effective use of the medication.
A further area of confusion arises due to the presence of various formulations and brands of medications. Generic drugs like Lorazepam are typically less expensive than their brand-name counterparts, which can lead patients to question whether they are receiving the same quality or efficacy. In this context, it is crucial to note that generic medications must meet the same regulatory standards set by health authorities, thereby ensuring comparable safety and effectiveness. Patients are encouraged to communicate openly with their healthcare providers regarding any concerns they may have about their prescribed medications, whether they refer to the brand name or the generic name.
Understanding the relationship between generic and brand names enhances a patient’s ability to manage their medication effectively and safely, thereby playing a vital role in their overall treatment plan.

Buying Lorazepam Online Safely
With the growing trend of purchasing medications online, it is essential to approach the acquisition of Lorazepam with caution. Lorazepam, commonly known by its brand name Ativan, is a medication that requires careful consideration when buying online. UKmedsolutions.com is one of the platforms where patients can acquire this medication, but diligence is necessary to ensure a safe purchase.
The first step in safely purchasing Lorazepam online is to verify the credibility of the pharmacy. A legitimate online pharmacy will typically require a valid prescription from a licensed healthcare provider. This requirement cannot be overlooked, as it helps ensure that the medication is appropriate for the patient’s condition. It is advisable to seek pharmacies that are certified or accredited by relevant regulatory authorities, which can often be found on the pharmacy’s website. Look for seals of approval or membership in the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP).
Another critical factor to consider is the website’s privacy policy. Ensure that the online pharmacy has a robust policy in place to protect personal and financial information. Secure websites will typically have ‘https://’ in the URL, which indicates that the site employs encryption to protect data during transmission. Additionally, be wary of pharmacies that offer Lorazepam without requiring a prescription or those that advertise the medication at significantly discounted prices, as these can be red flags for illegitimate operations.
Lastly, it is imperative to remain vigilant about the potential risks associated with obtaining medications online. Unregulated sources may sell counterfeit or substandard products that can pose serious health risks. Therefore, exercising caution while purchasing Lorazepam online is vital to ensure one’s health is not compromised. Engaging in thorough research and using reputable services like UKmedsolutions.com can provide the assurance needed for safe online transactions.
How Many Lorazepam Equals a Xanax?
When evaluating the conversion between ativan Lorazepam and Alprazolam, it is essential to understand that these two medications, while both belonging to the benzodiazepine class, have different potencies and pharmacokinetics. Lorazepam is typically prescribed for anxiety, insomnia, and sedation, whereas Alprazolam, commonly referred to by its brand name Xanax, is primarily used to manage anxiety disorders, particularly panic disorders. Due to their varying strengths, clinicians often find it necessary to establish a conversion ratio when switching from one medication to the other.
In clinical practice, approximately 0.5 mg of Alprazolam is considered equivalent to 1 mg of Lorazepam. This means that if a patient is taking 1 mg of Lorazepam, the equivalent Alprazolam dosage would roughly be 0.5 In clinical practice, approximately 0.5 mg of Alprazolam is considered equivalent to 1 mg of Lorazepam. This means that if a patient is taking 1 mg of Lorazepam, the equivalent Alprazolam dosage would roughly be 0.5 mg. However, this conversion is not absolute and can vary based on individual patient factors, including tolerance, the duration of use, and the specific conditions being treated. Adjustments may be necessary to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing the risk of adverse effects.In clinical practice, approximately 0.5 mg of Alprazolam is considered equivalent to 1 mg of Lorazepam. This means that if a patient is taking 1 mg of Lorazepam, the equivalent Alprazolam dosage would roughly be 0.5 mg. However, this conversion is not absolute and can vary based on individual patient factors, including tolerance, the duration of use, and the specific conditions being treated. Adjustments may be necessary to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing the risk of adverse effects. However, this conversion is not absolute and can vary based on individual patient factors, including tolerance, the duration of use, and the specific conditions being treated. Adjustments may be necessary to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
It is critically important for patients to consult their healthcare provider before making any changes to their medication regimen. A healthcare professional can provide tailored advice and monitor for side effects during the conversion process. Additionally, factors such as the patient’s health history and any concurrent medications must be taken into account when determining the appropriate dosages for ativan Lorazepam and Xanax. Therefore, patients should engage in open discussions with their providers regarding their treatment plans and any concerns that may arise when considering a switch between these two medications.
Conclusion: Making Informed Choices
As we have explored the distinctions and similarities between ativan Lorazepam and Alprazolam, it becomes evident that both medications serve critical roles in managing anxiety and related disorders. Lorazepam is typically preferred for its longer half-life, making it suitable for conditions that require prolonged management, while Alprazolam is often utilized for its rapid onset, providing immediate relief for acute anxiety episodes. Each medication, however, carries its own risk of dependence and adverse effects, emphasizing the need for careful consideration.
In understanding these medications, it is crucial to acknowledge that the choice between ativan Lorazepam and Alprazolam is not merely clinical but highly individualized. Various factors, including the specific anxiety disorder being treated, the patient’s medical history, potential interactions with other medications, and personal response to treatment, all play significant roles in determining the most appropriate option. This individualized approach reinforces the necessity of consulting healthcare professionals who can evaluate the comprehensive aspects of a patient’s health.
Moreover, understanding the implications of using either ativan Lorazepam or Alprazolam is paramount for safe and effective treatment. It is essential for patients to engage in open discussions with their healthcare providers about their symptoms, treatment expectations, and any concerns regarding the medications. This collaborative dialogue can facilitate informed choices, significantly impacting treatment outcomes and overall well-being.
In conclusion, both Lorazepam and Alprazolam have their advantages and limitations, and making an informed choice hinges on thorough knowledge and professional guidance. Patients should prioritize understanding their unique needs and work closely with healthcare providers to develop a sound treatment plan tailored specifically for them. This proactive approach ensures that they achieve the best possible results while minimizing risks associated with these medications.


Leave A Comment